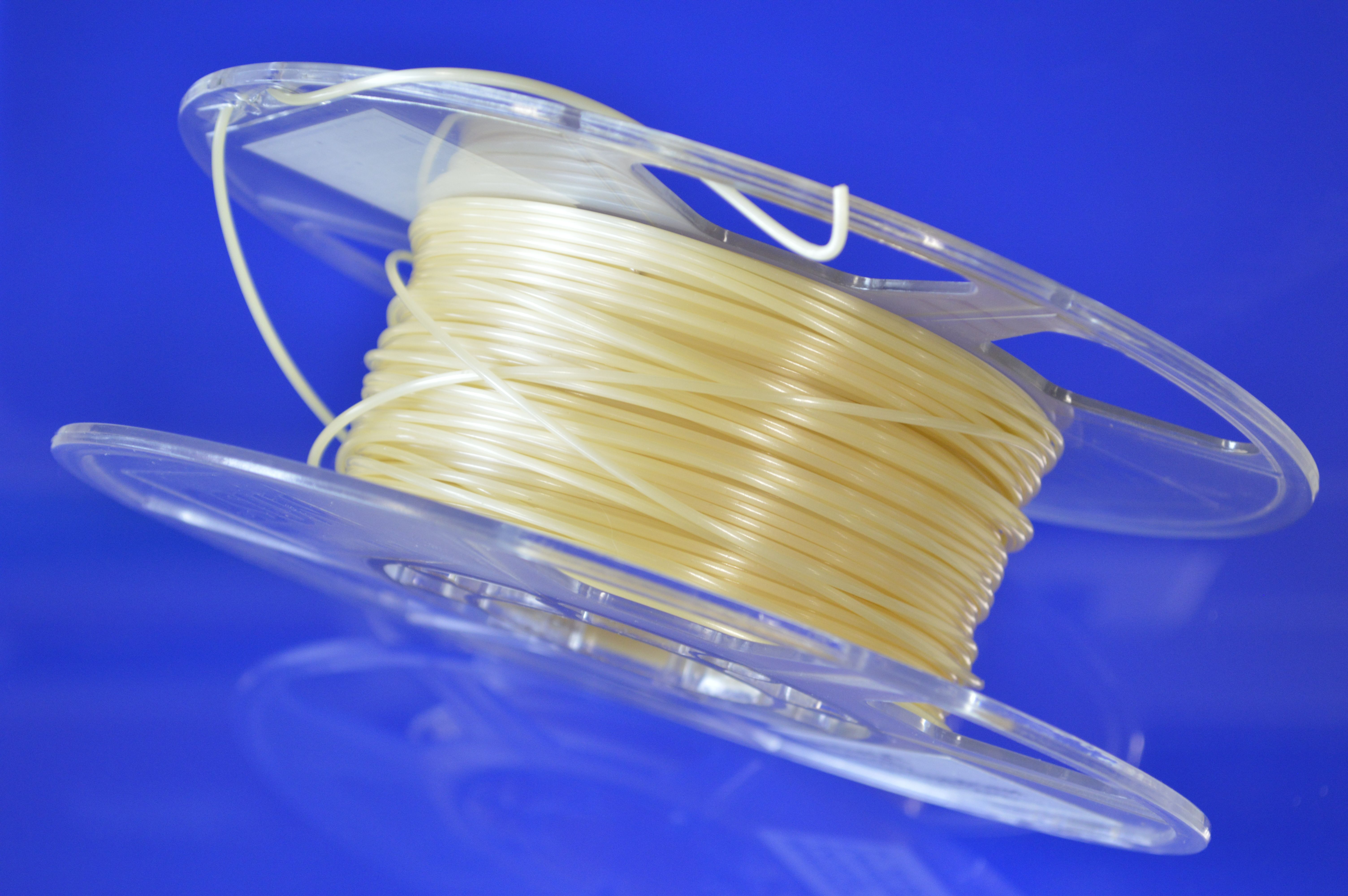
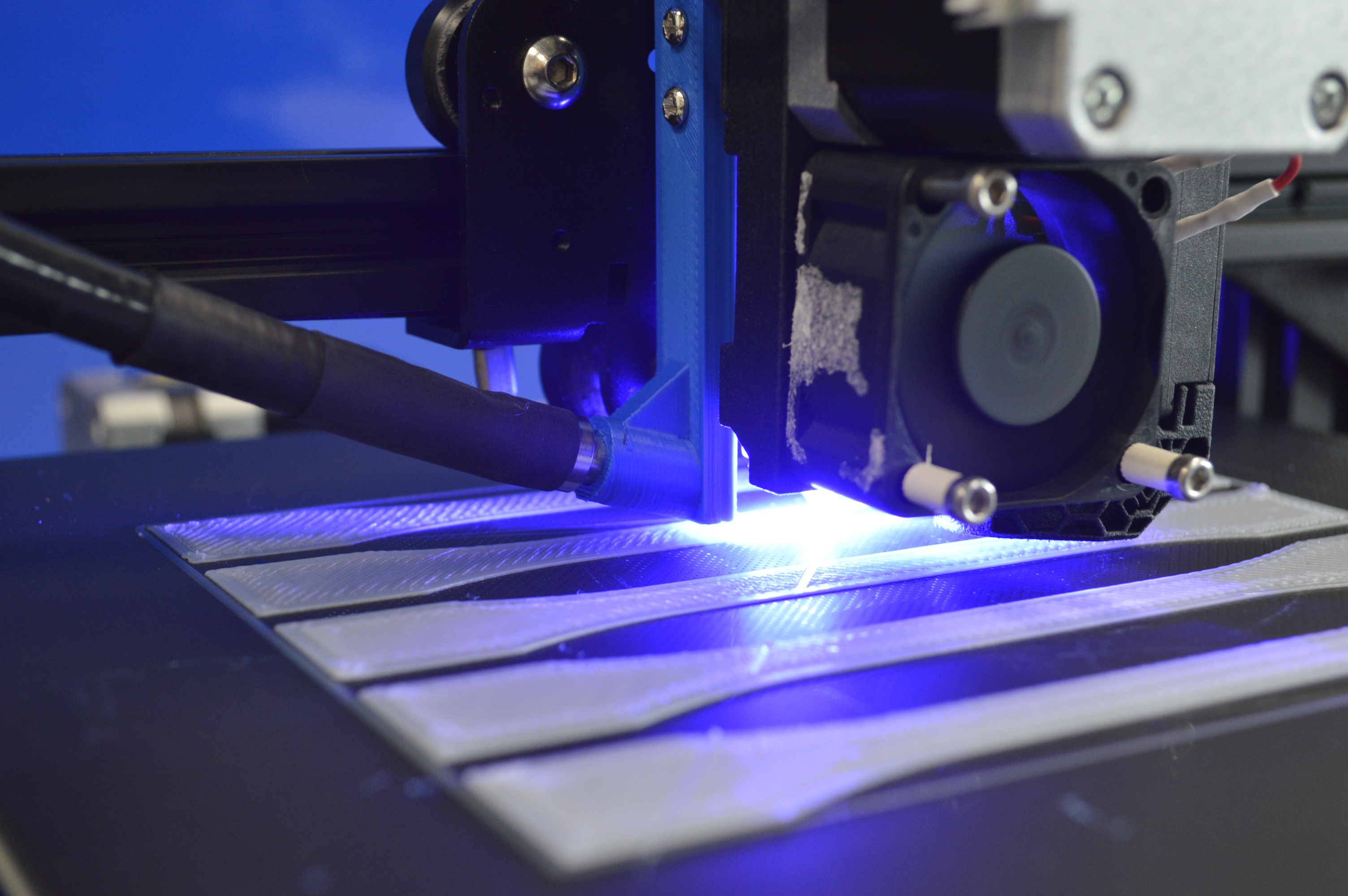
Additive manufacturing technologies are gaining increasing importance in the industry, particularly in series production. With the wide range of applications, the demands for new materials are also growing. Extrusion-based 3D printing processes, especially Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), play a key role here – especially in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Within the Reactive Printing project, latent reactive filaments based on epoxy resin are being developed. These innovative materials can be processed at low temperatures and crosslinked directly during the printing process to form thermoset components. This approach combines the easy processability of thermoplastic materials with the advantages of thermoset properties.
Current Challenges in the Use of Thermoplastic Filament Materials
The use of thermoplastic filament materials often leads to quality issues in printed components. This is particularly the case when parts need to withstand high temperatures in use. Often, high-performance thermoplastics (such as PEI, PEEK, or PPSU) are employed, which require high processing temperatures. This leads to significant temperature gradients between the print nozzle and the part surface, high thermal stresses, insufficient layer adhesion, warping and dimensional deviations in the printed part due to shrinkage and distortion.
Research Objective
The development of epoxy resin-based filaments aims to address these challenges. The materials are characterized by the following properties:
- Reduced anisotropic material properties through improved layer adhesion
- Processing at lower temperatures without the need for high-performance thermoplastics
- Access to thermoset fiber composite parts using FFF printing
- Production of hybrid components by printing material-locking connections onto existing structures made of various materials
Approach
In "Reactive Printing", Fraunhofer IFAM focuses on resin formulation for filament production as well as on material characterization. Furthermore, Fraunhofer IFAM is setting up a printer in order to characterize print properties and printing test components, which will be available as demonstrator after project. In cooperation, SKZ is mainly responsible for filament production and characterization, for which a demonstration facility is being set up. Additionally, SKZ conducts numerical simulations on the melting and extrusion behavior of crosslinkable compounds and characterizes the properties of the components. Upon project completion, the process chain will be evaluated using application-relevant components.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM
Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM