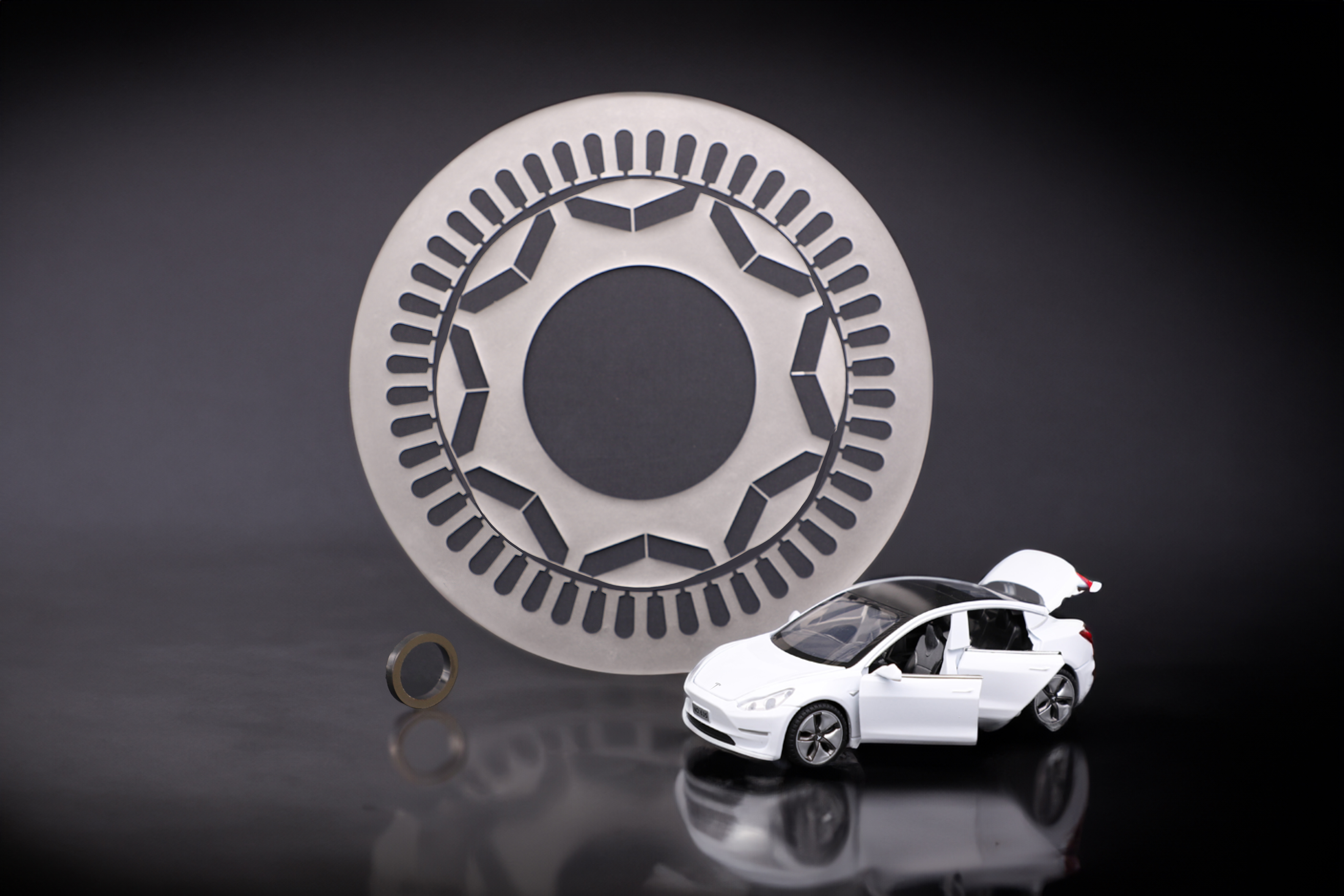
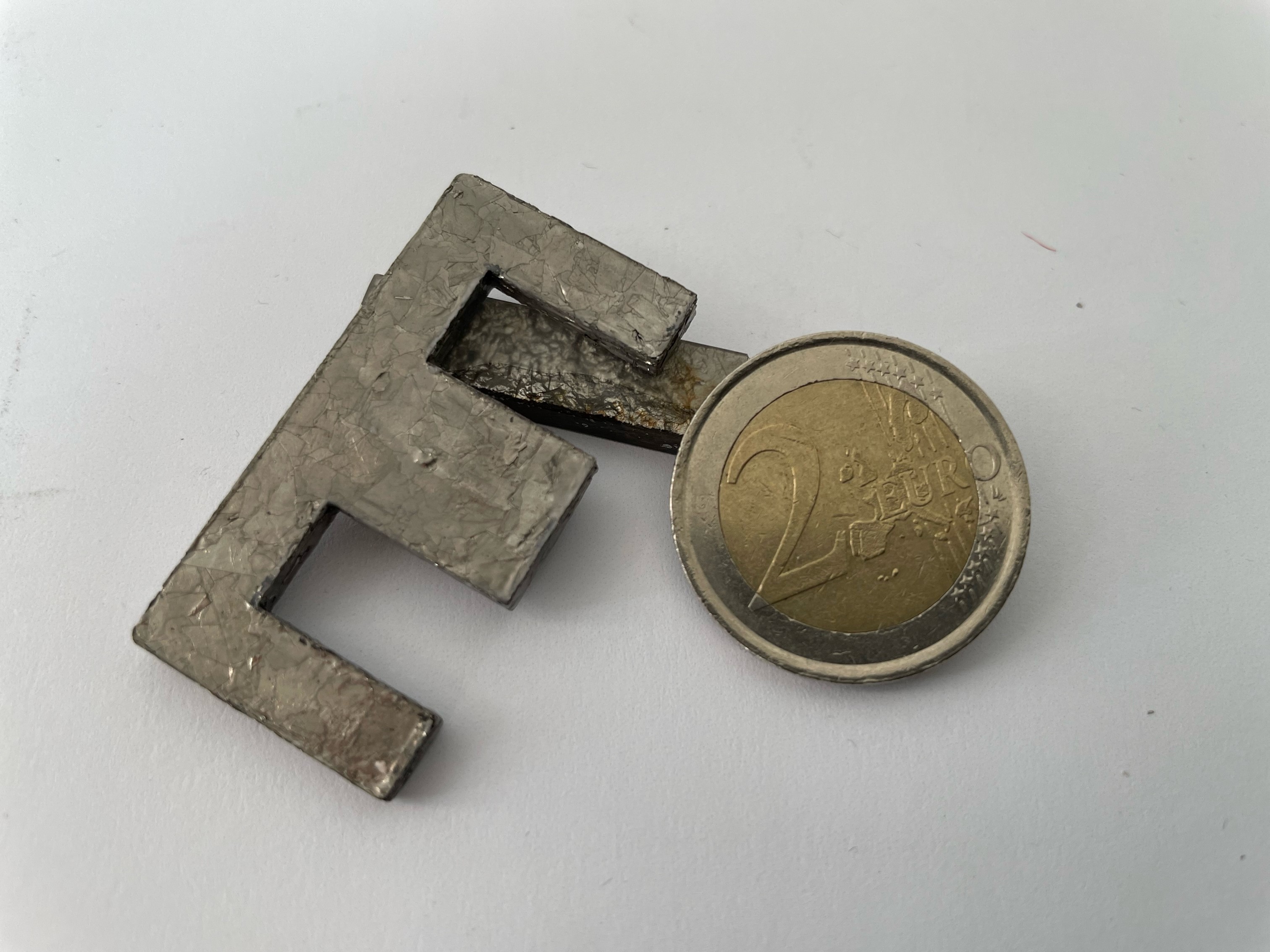
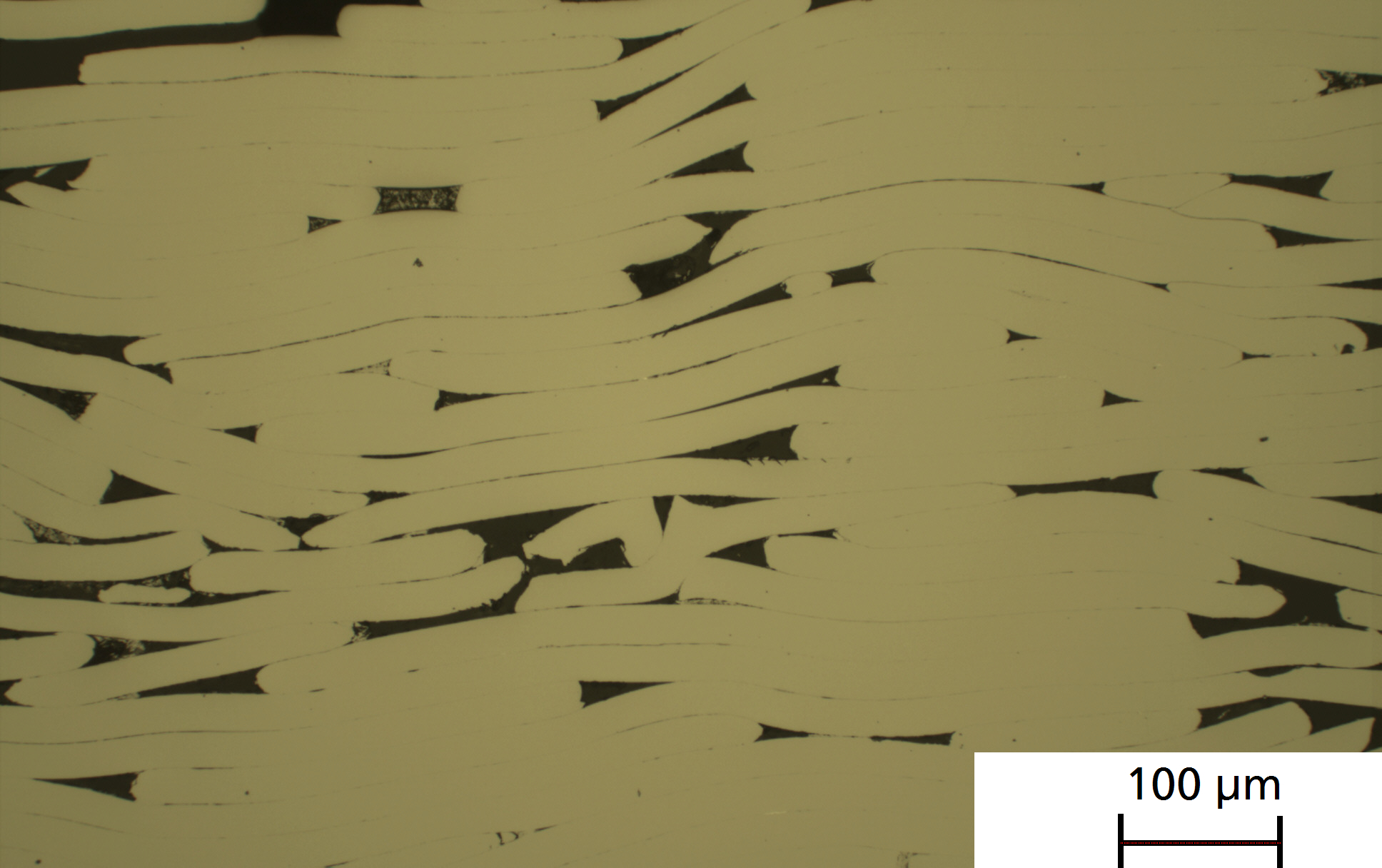
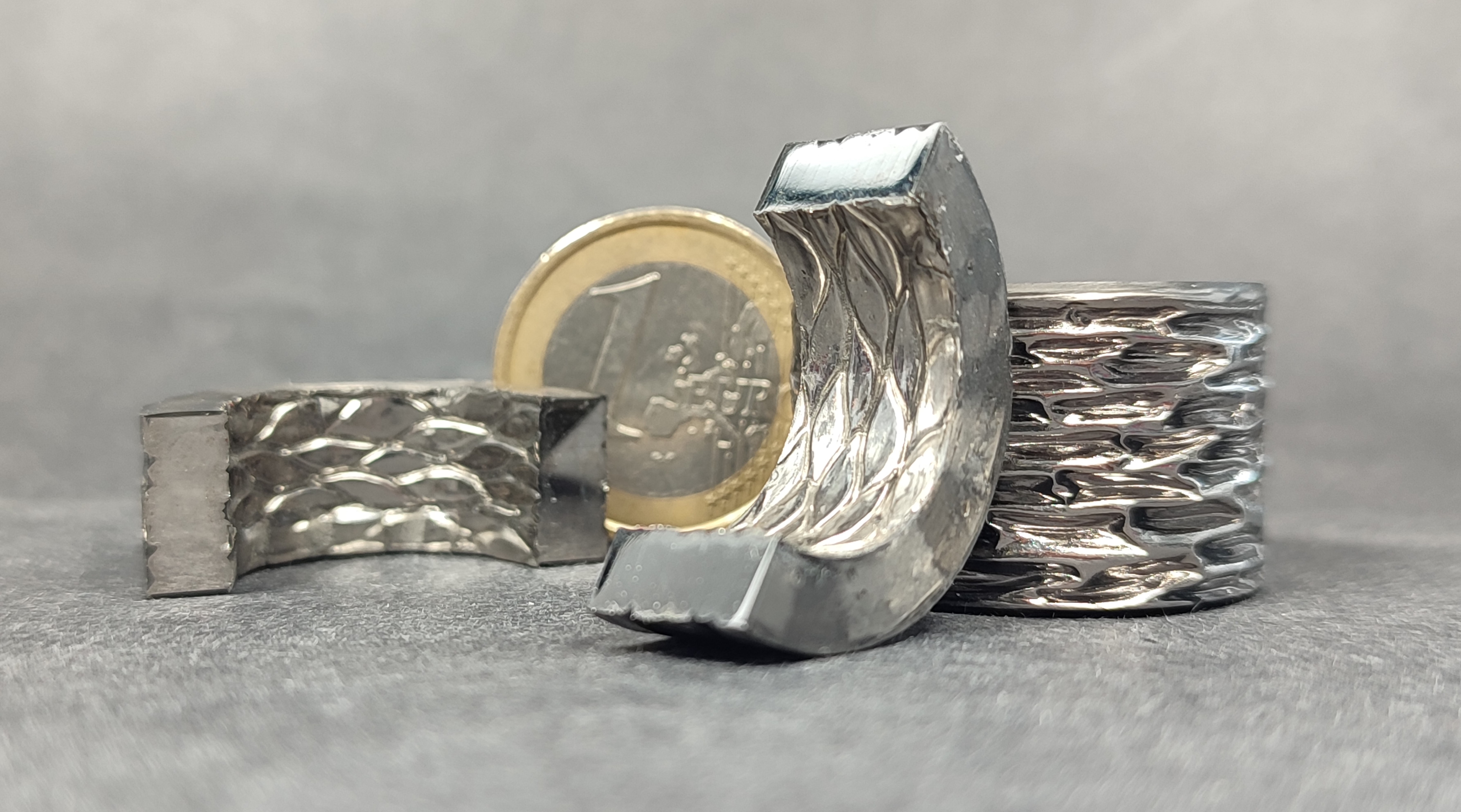
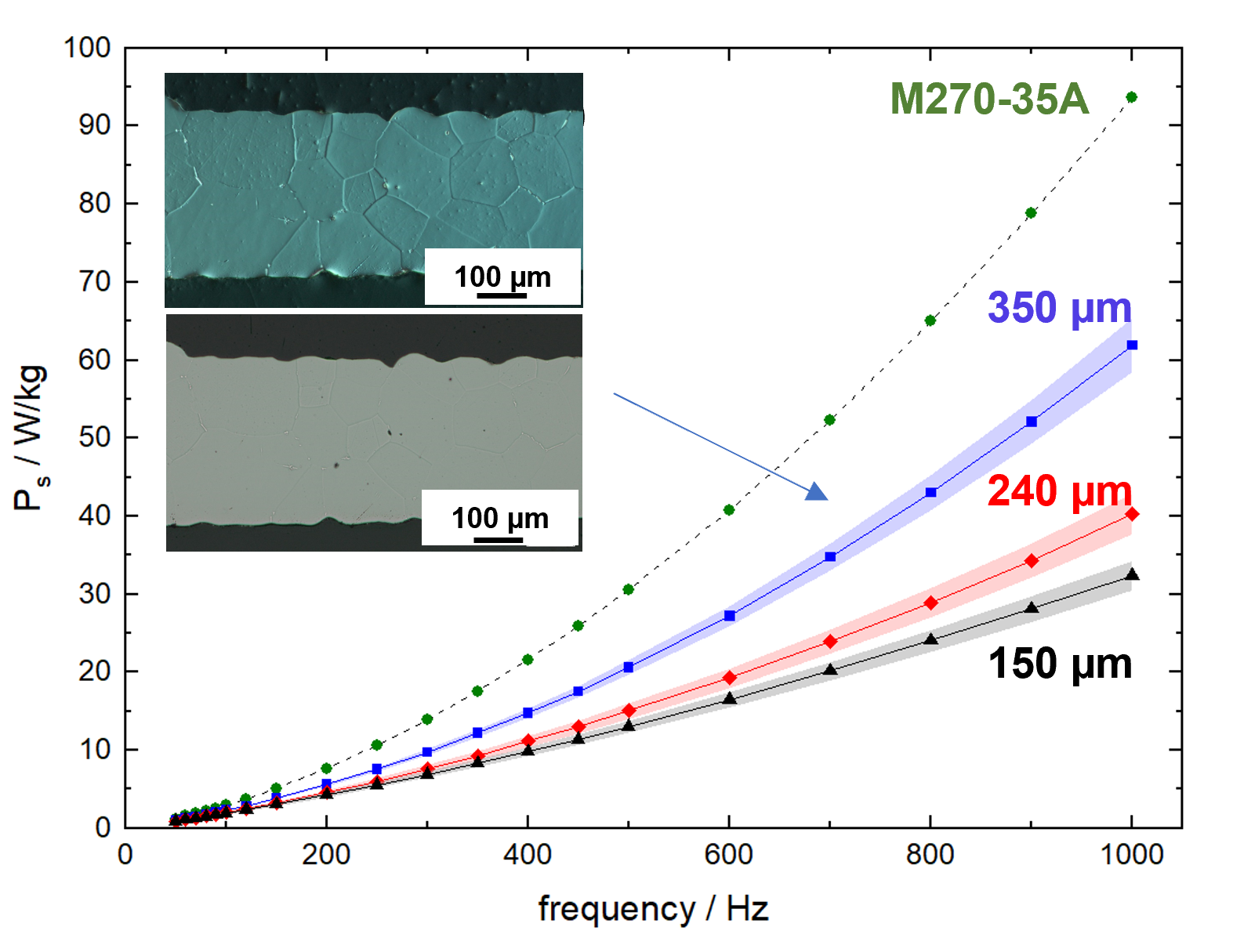
Powder metallurgical manufacturing concepts offer a wide range of possibilities to produce soft magnetic components that go far beyond traditional manufacturing technologies. Thus, soft magnetic components with a special property profile can be manufactured in alternative geometries. Focus of the work is the reduction of iron losses while increasing magnetic performance using near net shape manufacturing strategies.
Different powder metallurgical manufacturing concepts are pursued to address the application-specific characteristics. All methods have in common that the choice of materials is broader and the integration of additional functions is possible.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM
Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM