Methods for applying sealant to bipolar plates using screen printing



Fraunhofer IFAM is your competent partner for innovative research services in the field of fuel cell production. In addition to industrial projects in this context, we are active in public research projects - including the National Action Plan for Fuel Cell Production (H2GO). The National Action Plan maps the key sensitivities of the value chain in the production, stacking and recycling of substantial fuel cell components. Fraunhofer IFAM is, among other things, researching the use of the screen printing process for applying sealants to bipolar plates, which has several other advantages in addition to reducing production costs.
Fuel cell stacks should be able to be dismantled fully automatically
In the Stack 2P technology sub-network, the research objective of Fraunhofer IFAM is to modify fuel cell stacks, consisting of bipolar plates and MEA units, surface and bonding techniques in such a way that the fully automated dismantling of the thin layers is guaranteed after operation, despite polymer seals that are strongly adhesive due to the operating conditions. To this end, we assemble the bipolar plates and MEA units treated using plasma and VUV technology into stacks and subject them to a usage simulation. Subsequently, proof of safe dismantling is provided in order to make future recycling processes more efficient by separating components.
For the following practical investigations, the production technology requirements for the individual construction of fuel cell stacks must first be realized at Fraunhofer IFAM. Among many aspects, the focus is on the cycle time-adapted adhesive application by means of screen printing.
Screen printing as an innovative method for the high-precision application of adhesives
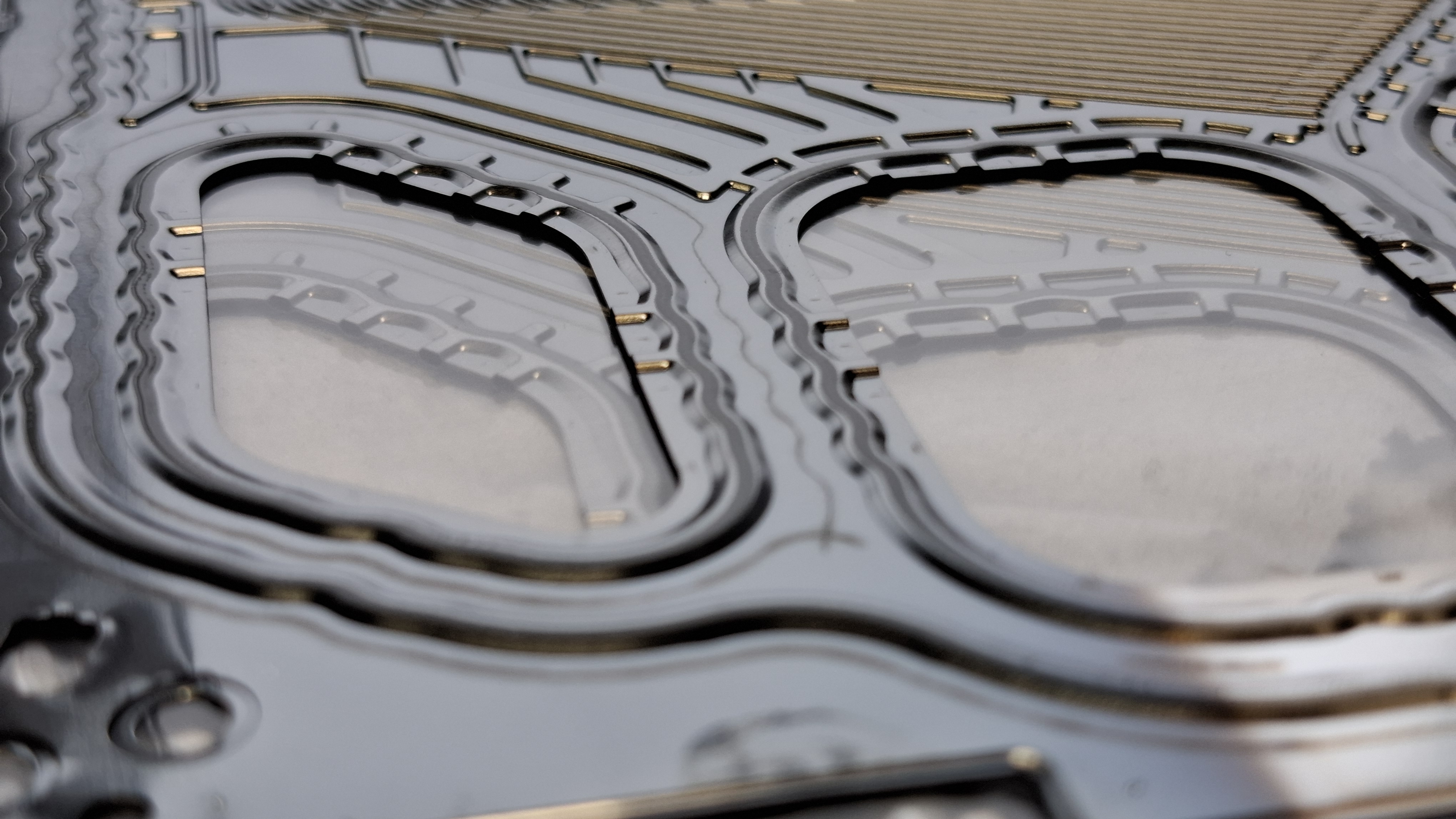
Due to the sometimes several hundred sealing layers in the overall stack between the bipolar plates and MEA units, high-rate application processes must be used in the future that can apply sealant of the most complex geometries in a defined layer thickness within seconds. This possibility is offered by the screen printing process, which we can now fully reproduce at Fraunhofer IFAM for e.g. metallic bipolar plates of the generic stack of the ZSW Center for Solar Energy and Hydrogen Research Baden-Württemberg.
The screen printing process is an innovative method for the high-precision application of adhesives to bipolar plates and is being intensively researched at Fraunhofer IFAM. By using a fine-mesh screen with a barrier layer adapted to the bead geometry, the adhesives can be applied to the embossed sealing bead of the bipolar plate in precisely defined patterns and quantities. This enables precise and controlled application, which is ideal for the high-rate, fully automated production of fuel cells within very short cycle times.
The advantages of this technology are manifold:
- Firstly, screen printing offers high precision, which significantly improves the consistency and quality of the components produced.
- Secondly, the process is characterized by efficiency and speed, which allows us to significantly reduce production costs in the application.
- Thirdly, the targeted application of adhesive leads to material savings, as the adhesive can be applied in a defined layer thickness and with tight tolerances and can also be cured openly as a CIPG seal, thus offering a cost-effective alternative to the technically complex overmolding in the injection molding process.
In addition to the actual screen printing process, we offer comprehensive expertise in material selection and qualification in the context of the fuel cell sealant application. This includes:
 Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM
Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Technology and Advanced Materials IFAM